Acute Pancreatitis
Background
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. It can be caused by impacted gallstones in the bile duct, heavy alcohol use (30% of cases), systemic disease, trauma and in children due to mumps.
Although mild cases can be treated with pain control and IV nutritional support, severe cases often require hospitalization/intensive care to manage the complications of this disease. Complications are often associated with high mortality, even with optimal care. Although the symptoms are vast, the most common symptom is upper abdominal pain. Patients with severe AP (15 to 20% of cases) require prolonged intensive care stays and multiple invasive procedures. Although there have been moderate advances, severe AP is associated with a mortality rate of 20-25%. Severe AP is an inflammatory disease.
In the United States, there are more than 300,000 hospital stays in the United States each year related to AP.
The Theratome Solution
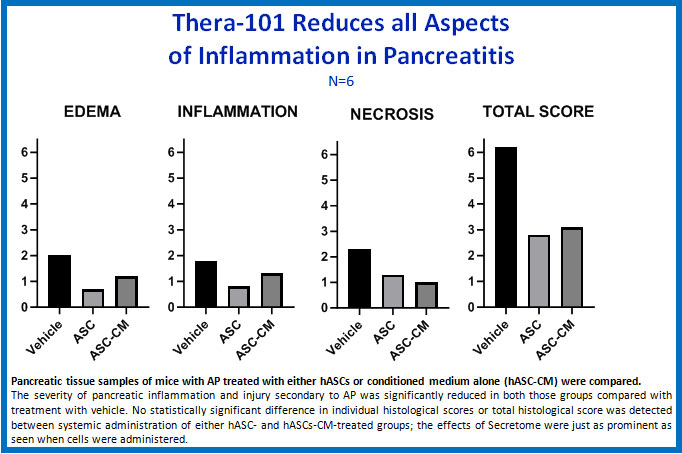
Animal studies have shown that IV delivery of human adipose stem cell secretome markedly reduces pancreatic inflammation and necrosis, as shown in below. The mechanisms involved in this effect appear to be macrophage polarization toward M2 anti-inflammatory macrophage phenotype and by a paracrine effect.